Medical technologies
Using the latest treatment technologies
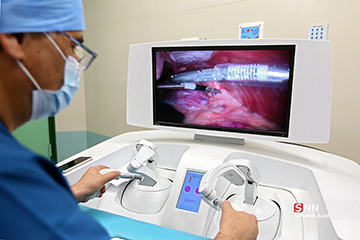
The robotic system allows surgeons to perform procedures remotely from thousands of kilometers away in situations where patient transfer is dangerous and difficult.
The robotic surgical system consists of two main components: a remote surgical console and surgical robots stationed at the patient's bedside. The surgical robot features 23 joints equipped with electric motors capable of performing the most delicate surgical tasks. The surgical console includes a monitor, two leader robots, and foot control pedals, allowing the surgeon to observe images from the surgical area and remotely control the surgical instruments and imaging camera.
On the other hand, three follower robots, consisting of two instrument-carrying robots and one imaging robot stationed at the patient’s bedside, execute the surgeon's commands. During the operation, the imaging robot, controlled by the surgeon, provides images of the surgical area at the surgical console, while the movements of the surgeon's hands are captured by the leader robots, which filter out tremors and scale the movements to be transmitted to the follower robots for precise execution at the surgical site.
The robotic surgical system underwent technical and functional tests and was evaluated in animal testing. Common procedures performed using this system on live animals (under complete anesthesia in a setting similar to human operating rooms) include hysterectomy, vasectomy, and laparoscopic cholecystectomy, which involves removing the gallbladder through three five-millimeter incisions on the animal's abdomen.
انتخاب حالت کور رنگی
سرخ کوری سبز کوری آبی کوری سرخ دشوار بینی سبز دشوار بینی آبی دشوار بینی تک رنگ بینی تک رنگ بینی مخروطیتغییر اندازه فونت:
تغییر فاصله بین کلمات:
تغییر فاصله بین خطوط:
تغییر نوع موس:

